中国沙漠 ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (5): 1-8.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2023.00012
• •
收稿日期:2022-12-04
修回日期:2023-02-09
出版日期:2023-09-20
发布日期:2023-09-27
作者简介:何晨晨(1994—),男,陕西咸阳人,博士研究生,主要从事风沙地貌与风沙工程研究。E-mail: hechenchen22@mails.ucas.ac.cn
基金资助:
Chenchen He1,2( ), Yingying Wu1,2, Zhenting Wang1
), Yingying Wu1,2, Zhenting Wang1
Received:2022-12-04
Revised:2023-02-09
Online:2023-09-20
Published:2023-09-27
摘要:
风蚀导致的土地退化是全球性问题,跃移颗粒对地表冲击是关键的土壤风蚀过程。目前,土壤团聚体在跃移运动中的破碎过程和机制尚未完全被揭示。通过室内模拟实验,探讨干燥致密的土壤团聚体在与地面碰撞时的临界破碎速度与粒径分布规律。结果表明:(1)低速冲击下,土壤团聚体与地面碰撞过程中主要以损伤状态为主,碰撞产生的裂纹沿经线平面形成贯穿裂纹;较高速度下,碰撞接触区出现锥形体导致团聚体破碎。(2)粒径、密度、抗压强度和杨氏模量共同决定临界碰撞速度。由量纲理论和实验数据给出了具体的函数关系与经验常数。(3)碰撞过程中,壤土粉尘释放量随速度变化显著,黏土、砂土、砂质黏土、壤质黏土的粉尘释放量大部分小于团聚体质量的1%。(4)碰撞后的碎片分布规律可由双参数Weibull累积分布函数描述。由于存在内部缺陷,土壤团聚体碎片分散性不同于玻璃、陶瓷等常规脆性材料。
中图分类号:
何晨晨, 吴盈盈, 王振亭. 土壤团聚体与地面碰撞时的临界破碎速度与粒径分布[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(5): 1-8.
Chenchen He, Yingying Wu, Zhenting Wang. Threshold velocity and fragment size distribution for the rupture of soil aggregates colliding with land surface[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(5): 1-8.
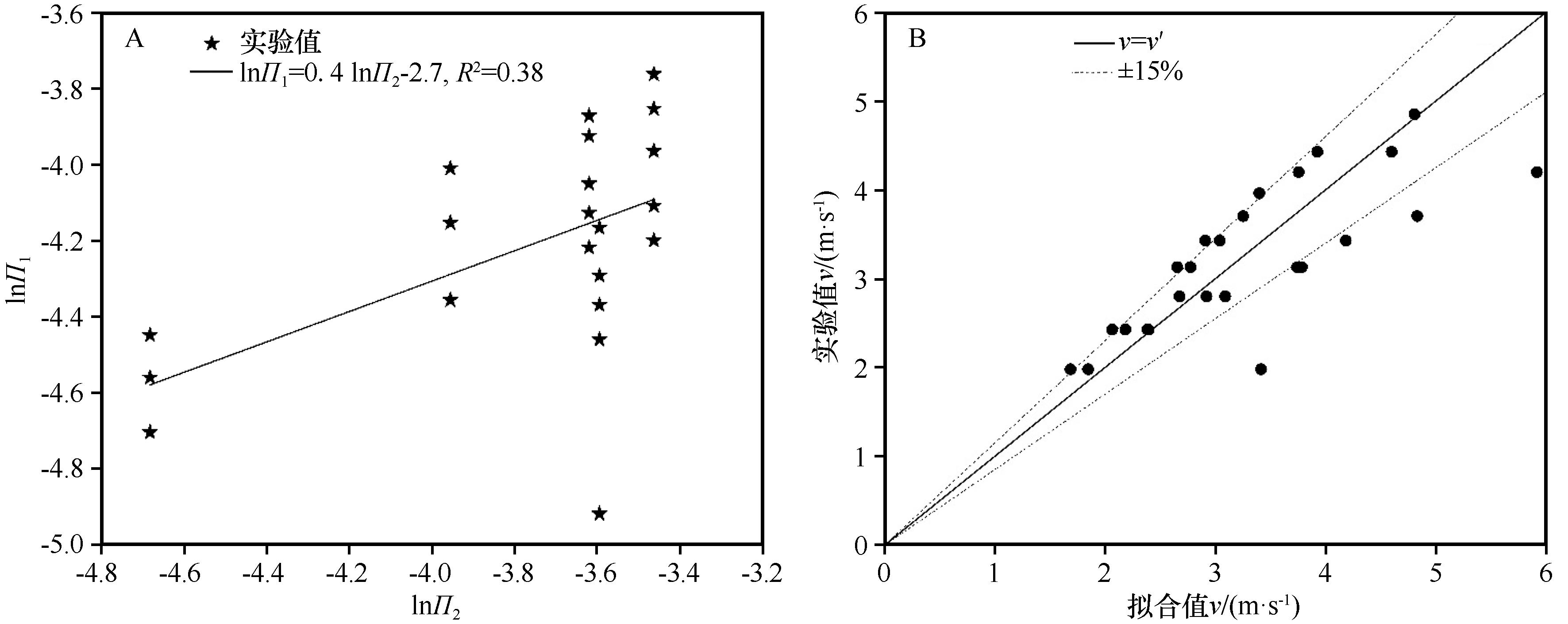
图4 无量纲参数Π1与Π2线性拟合(A)及拟合值与实验值对比(B)
Fig.4 Linear fit of dimensionless parameter Π1 to Π2 (A) and comparison of fitted values and experimental values (B)
| 土壤 类型 | 粒径 /cm | 样本数 /个 | 释放高度 /cm | 各高度释放 次数 | 碎片数量 /个 | 土壤 类型 | 粒径 /cm | 样本数 /个 | 释放高度 /cm | 各高度释放 次数 | 碎片数量 /个 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黏土 | 2 | 6 | 90~140 | 1 | 15 | 砂土 | 5 | 4 | 90~120 | 1 | 27 |
| 3 | 6 | 80~130 | 1 | 27 | 6 | 5 | 70~110 | 1 | 24 | ||
| 4 | 6 | 70~120 | 1 | 56 | 壤质黏土 | 2 | 6 | 60~110 | 1 | 31 | |
| 5 | 6 | 60~110 | 1 | 79 | 3 | 7 | 50~110 | 1 | 31 | ||
| 6 | 6 | 30~80 | 1 | 65 | 4 | 5 | 50~90 | 1 | 33 | ||
| 壤土 | 2 | 5 | 60~100 | 1 | 21 | 5 | 6 | 40~90 | 1 | 54 | |
| 3 | 6 | 40~90 | 1 | 33 | 6 | 6 | 40~90 | 1 | 46 | ||
| 4 | 6 | 40~90 | 1 | 40 | 砂质黏土 | 2 | 6 | 110~160 | 1 | 20 | |
| 5 | 6 | 30~80 | 1 | 37 | 3 | 7 | 90~150 | 1 | 38 | ||
| 6 | 6 | 30~80 | 1 | 52 | 4 | 4 | 90~120 | 1 | 29 | ||
| 砂土 | 2 | 6 | 140~220 | 1 | 27 | 5 | 7 | 70~130 | 1 | 53 | |
| 3 | 6 | 100~200 | 1 | 47 | 6 | 8 | 50~120 | 1 | 54 | ||
| 4 | 6 | 100~200 | 1 | 49 |
表1 不同土壤类型团聚体碎片统计
Table 1 Aggregate debris statistics of different soil types
| 土壤 类型 | 粒径 /cm | 样本数 /个 | 释放高度 /cm | 各高度释放 次数 | 碎片数量 /个 | 土壤 类型 | 粒径 /cm | 样本数 /个 | 释放高度 /cm | 各高度释放 次数 | 碎片数量 /个 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黏土 | 2 | 6 | 90~140 | 1 | 15 | 砂土 | 5 | 4 | 90~120 | 1 | 27 |
| 3 | 6 | 80~130 | 1 | 27 | 6 | 5 | 70~110 | 1 | 24 | ||
| 4 | 6 | 70~120 | 1 | 56 | 壤质黏土 | 2 | 6 | 60~110 | 1 | 31 | |
| 5 | 6 | 60~110 | 1 | 79 | 3 | 7 | 50~110 | 1 | 31 | ||
| 6 | 6 | 30~80 | 1 | 65 | 4 | 5 | 50~90 | 1 | 33 | ||
| 壤土 | 2 | 5 | 60~100 | 1 | 21 | 5 | 6 | 40~90 | 1 | 54 | |
| 3 | 6 | 40~90 | 1 | 33 | 6 | 6 | 40~90 | 1 | 46 | ||
| 4 | 6 | 40~90 | 1 | 40 | 砂质黏土 | 2 | 6 | 110~160 | 1 | 20 | |
| 5 | 6 | 30~80 | 1 | 37 | 3 | 7 | 90~150 | 1 | 38 | ||
| 6 | 6 | 30~80 | 1 | 52 | 4 | 4 | 90~120 | 1 | 29 | ||
| 砂土 | 2 | 6 | 140~220 | 1 | 27 | 5 | 7 | 70~130 | 1 | 53 | |
| 3 | 6 | 100~200 | 1 | 47 | 6 | 8 | 50~120 | 1 | 54 | ||
| 4 | 6 | 100~200 | 1 | 49 |
| 1 | Shi P, Yan P, Yuan Y,et al.Wind erosion research in China:past,present and future[J].Progress in Physical Geography,2004,28(3):366-386. |
| 2 | 吴正.风沙地貌和治沙工程学[M].北京:科学出版社,2003:31-75. |
| 3 | 张春来,宋长青,王振亭,等.土壤风蚀过程研究回顾与展望[J].地球科学进展,2018,33(1):27-41. |
| 4 | 董治宝.中国风沙物理研究50a(I)[J].中国沙漠,2005,25(3):293-305. |
| 5 | 董治宝,郑晓静.中国风沙物理研究50a(II)[J].中国沙漠,2005,25(6):795-815. |
| 6 | Shao Y.Physics and Modelling of Wind Erosion[M].Heidelberg,Germany:Springer,2008:117-246. |
| 7 | Bagnold R.The Physics of Blown Sand and Desert Dunes[M].New York,USA:William Morrow & Company,1941:85-95. |
| 8 | Shao Y, Lu H.A simple expression for wind erosion threshold friction velocity[J].Journal of Geophysical Research,2000,105(D17):22437-22443. |
| 9 | Lu H, Shao Y.A new model for dust emission by saltation bombardment[J].Journal of Geophysical Research,1999,104(D14):16827-16842. |
| 10 | Greeley R, Leach R N, Williams S H,et al.Rate of wind abrasion on Mars[J].Journal of Geophysical Research,1982,87(B12):10009-10024. |
| 11 | 贾晓鹏,王海兵.土壤表面划痕与颗粒碰撞磨蚀实验研究[J].中国沙漠,2009,29(2):219-222. |
| 12 | Wang Z, Wang H, Niu Q,et al.Abrasion of yardangs[J].Physical Review E,2011,84(3):31304. |
| 13 | Wang Z.Erosion model for brittle materials under low speed impacts[J].Journal of Tribology,2020,142(7):74501. |
| 14 | 吴盈盈,刘旭阳,王振亭.干燥致密土壤在沙粒流冲击下的磨蚀规律[J].农业工程学报,2022,38(8):315-320. |
| 15 | Kok J F.A scaling theory for the size distribution of emitted dust aerosols suggests climate models underestimate the size of the global dust cycle[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,2011,108(3):1016-1021. |
| 16 | Carneiro M V, Araújo N A M, Pähtz T,et al.Midair collisions enhance saltation[J].Physical Review Letter,2013,111(5):58001. |
| 17 | Buckingham E.On physically similar systems: illustrations of the use of dimensional equations[J].Physical Review,1914,4(4):345. |
| 18 | Sanchidrián J A, Ouchterlony F, Segarra P,et al.Size distribution functions for rock fragments[J].International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences,2014,71(8):381-394. |
| 19 | 陈兴,马刚,周伟,等.无序性对脆性材料冲击破碎的影响[J].物理学报,2018,67(14):219-228. |
| 20 | Kohout J.Three-parameter Weibull distribution with upper limit applicable in reliability studies and materials testing[J].Microelectronics Reliability,2022,137:114769. |
| 21 | 曹立悦,李玉霖,詹瑾,等.开垦对科尔沁沙地土壤团聚体分布及稳定性的影响[J].中国沙漠,2021,41(2):212-220. |
| 22 | Sun H, Ye Y, Zeng Y,et al.Experimental study on the fragment characteristics of marble spheres under repeated impacts[J].Engineering Geology,2021,289:106162. |
| 23 | Tomas J, Schreier M, Gröger T,et al.Impact crushing of concrete for liberation and recycling[J].Powder Technology,1999,105(1/3):39-51. |
| 24 | 周强,肖庆飞,潘永泰.挤压作用下脆性物料断裂强度分布研究[J].中国矿业大学学报,2022,51(6):1086-1095. |
| 25 | Pisano G, Carfagni G R.The statistical interpretation of the strength of float glass for structural applications[J].Construction and Building Materials,2015,98(15):741-756. |
| 26 | King D S, Fahrenholtz W G, Hilmas G E.Silicon carbide-titanium diboride ceramic composites[J].Journal of the European Ceramic Society,2013,33(15/16):2943-2951. |
| [1] | 许瑞聪, 董治宝, 南维鸽, 陈国祥, 杨馥宁, 孔玲玲. 柴达木盆地南缘死亡蛛丝蓬( Halogeton arachnoideus )风影沙丘形态和沉积特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(4): 55-63. |
| [2] | 郭雪阳, 杨林海, 程良清, 胡光印, 胡菁菁. 河西走廊酒东沙地风沙沉积物理化特征及其环境意义[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(4): 17-30. |
| [3] | 王耀宗, 岳新斌, 谢家丽, 刘志鹏, 马媛, 王亚晖, 宫燕. 2000—2020年宁夏河东沙区沙漠化演变[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(4): 31-40. |
| [4] | 罗霖炎, 高鑫, 赵永成. 新月形沙丘表面流场特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(4): 41-54. |
| [5] | 王涛. 中国防沙治沙实践与沙漠科学发展的70年——Ⅱ.开拓篇 (2)[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(3): 1-8. |
| [6] | 赵鸿雁, 颜长珍, 李森, 王亚晖. 黄河流域2000—2020年土地沙漠化遥感监测及驱动力分析[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(3): 127-137. |
| [7] | 李琦炜, 龚志军, 罗明, 彭花明, 王瀚, 王威. 鄱阳湖沙山两处具有平行层理砂层的粒度分析及其对沉积环境的指示意义[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(3): 152-159. |
| [8] | 范亚伟, 杜鹤强, 卢善龙, 韩致文, 刘秀帆, 刘欣雷. 长江源卓乃湖流域地表沉积物粒度分布与风沙流结构[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(3): 47-56. |
| [9] | 肖雨婷, 张国明, 洪畅, 刘连友, 杨岩岩, 谷雨, 刘勇, 向明珠, 曲书锋, 孙煦然. 巴丹吉林沙漠西缘不同地表沙尘水平通量[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(2): 104-113. |
| [10] | 曲书锋, 张国明, 董苗, 徐俊泉, 尚鹏, 严平, 刘连友, 杜洁雯. 阿尔金山国家级自然保护区东北部风况及输沙势特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(2): 114-120. |
| [11] | 黄日辉, 张立婷, 冯淼彦, 刘铮瑶, 李健熙, 陈韵琪, 张志浩, 王璟. 广东省东海岛大岭剖面沉积物粒度、微形态特征与沉积环境[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(2): 121-129. |
| [12] | 张正偲, 潘凯佳, 张焱, 韩兰英. 中国西北戈壁区沙尘暴过程中近地层风沙运动特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(2): 130-138. |
| [13] | 陈京平, 余子莹, 杨帆, 王蜜, 胡涵, 倪观忠, 高鑫, 王鑫. 塔克拉玛干沙漠腹地沙尘暴和地表沙物质粒度特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(2): 150-158. |
| [14] | 陈书峄, 张伟民, 马绍休, 谭立海, 梁林昊. 戈壁近地表粉尘释放动力机制的野外风洞试验[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(2): 216-225. |
| [15] | 李静芸, 傅天阳, 申玉龙, 王立辉, 伍永秋. 毛乌素沙地新月形和抛物线形沙丘表层沉积物粒度特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(2): 226-232. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
